This is a map used to represent the top level domain (TLD) name system of the internet. The TLDs are visualized and linked as KML. The map and additional info on this project can be found at http://www.zook.info/tld_map.html
Tuesday, October 14, 2008
Map# 51: Remote Sensing Mapping
This is a map used to represent the top level domain (TLD) name system of the internet. The TLDs are visualized and linked as KML. The map and additional info on this project can be found at http://www.zook.info/tld_map.html
Sunday, October 12, 2008
Map# 50: Star Plots
Star Plots show multiple varying data. When combined with other star plots, the viewer can compare a variety of observations. This analysis shows star plots for 16 different 1979 automobile models comparing 9 different variables of Price, Mileage (MPG), 1978 Repair Record (1 = Worst, 5 = Best), 1977 Repair Record (1 = Worst, 5 = Best), Headroom, Rear Seat Room, Trunk Space, Weight, and Length.
Map# 49: Correlation Matrix
A Correlation Matrix shows the strength and direction of relationship between two variables, or simply put, how closely correlated two items under consideration are. In the financial world, this could be used to depict how closely related two different stocks are or, as this correlation matrix does, showing correlations between the S & P 500, 10 different sectors, gold, oil, and the 10 year Treasury note. The numbers in green show higher correlation than numbers in red.
Map# 48: Similarity Matrix
Map# 47: Stem and Leaf Plot
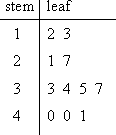
A Stem and Leaf Plot organizes data in order to show its shape and distribution. In this instance, the number 12 is depicted as 1 under the stem, and 2 under the leaf. Likewise, 13 is depicted as 1 under the stem and 3 under the leaf. This stem and leaf plot shows a distribution of 2 values between 10 and 19, 2 values between 20 and 29, 4 values between 30 and 39, and 3 values between 40 and 49. The largest distribution is between 30 and 39. This plot can be found at the following web site: http://www.glencoe.com/sec/math/studytools/cgi-bin/msgQuiz.php4?isbn=0-02-833050-1&chapter=2&lesson=6
Map# 46: Box Plot
Map# 45: Histogram
Map# 44: Parallel Coordinate Graph
Map# 43: Triangular Plot
Map# 42: Windrose
Map# 41: Climograph
Map# 40: Population Profile
Map# 39: Scatterplot
Map# 34: Univariate Choropleth Map
Map# 33: Bivariate Choropleth Map
Map# 32: Unclassed Choropleth Map
Map# 31: Classed Choropleth Map
Map# 30: Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Map# 29: Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map
Thursday, October 9, 2008
Map# 28: Digital Ortho Quarter Quads (DOQQ) Map.
Digital Orthophotos are images which depict a uniform scale. Because of this, it is possible to measure directly on it like other maps. These maps can be used as base maps for additional overlays for a variety of information. The example above is a 3-D view of Salem, NY. This map was produced with complicated mapping techniques detailed at Terrainmap.com edited by John Childs.
Wednesday, October 8, 2008
Map# 27: Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
DEMs are the most used basis for digitally produced relief maps. These maps are a digital representation of ground surface topography or various terrain. They are formed from either land surveying or, more often, remote sensing techniques. They are also called digital terrain models. Notice the level of detail that is obtained on the DEM map above.
Map# 26: Digital Line Graph (DLG)
Above is a DLG 1: 2,000,000 scale map of Missouri depicting Boundaries, hydrography, and roads. DLG maps are derived from USGS DLG databases. They are high resolution maps containing outlines of a variety of features such as: country and coast lines, state outlines, county outlines, roads, railroads, streams, lakes and islands, major city outlines, and military reservations to name a few.
Saturday, September 27, 2008
Map# 25: DRG
Map# 24: Isopleth Map
Isopleth maps generalize and simplifiy data with a continuous distribution. It shows the data as a third dimension on a map. These maps are often utilized for mapping surface elevations, amounts of precipitation, atmospheric pressure, and numerous other measurements that can be viewed statistically as a third dimension.
Map# 23: Isohyet Map
Map# 22: Isotach Map
Map# 21: Isobar Map
Map# 20: LIDAR
Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) is a remote sensing system used to collect topographic data. This system is being used to document topographic changes along shorelines. After establishing a baseline, scientists can then follow up in the future to detect shoreline changes. This map captures elevation data from Hilton Head, South Carolina to enable the study of shorelines changes there.
Map# 19: Doppler Radar Map
Map# 18: Black and White aerial photo map
Map# 17: Infrared Aerial Photo Map
This is an infrared aerial photo map of the United States. The photo was taken in the infrared band of light and shown on the National Weather Service web page. Lower level clouds are generally warmer. They are shown as grey areas. Higher clouds are usually colder and are shown as colored areas. Warmer objects are always darker.
Map# 16: Cartographic Animation
Cartographic animation is the incorporation of graphic art that occurs in time. Animation provides is a dynamic visual statement that evolves through various interval changes in the display. Using this type of mapping would allow viewers to observe changes in data over a period of time in a striking way. You could depict how an important battle proceeded, how railroads spread across the country, and how trade developed along them. These are just two examples. The map above shows how rainfall has changed in this portion of Africa over a period of years. (wait for animation to load).
Map# 15: Statistical Map
Map# 14: Cartogram
A cartogram is a map that resizes territories according to the variable which is being studied. The above map is a cartogram of the 2004 Presidential election results. Notice how the size of the states has been redrawn to reflect the actual size of their populations and not just their geographic size.
Map# 13: Flow Map
Map# 12: Isoline Map
Isoline maps show continuing lines joining points of like value. A common example is contour lines on a topographic map. Other examples include isobars showing barometric pressure, isotachs showing wind speed, and isotherms showing temperature. The colorful map above shows areas of common dewpoint temperatures throughout the United States.
Map# 11: Proportional Circle Map
Map# 10: Choropleth Map
Choropleth maps show quantitative data through the use of various colors and intensity of those colors. One can use this type of map to show density, percent, average value of a certain subject. The map above shows the net cash farm income throughout the United States. The darker the red, the higher the net cash income. Notice the high farm income in Southern California.
Map# 9: Dot Distribution Maps
Dot distribution maps highlight where particular data characteristics occur. These maps utilize dots or various other markers to represent the number of occurrences of a certain data characteristic in a location or area. Each dot or symbol used on the map may represent a single entity (one dot = one person) or a group (one dot = 1000 people). The map above shows acres of farmland with 1 dot equalling 100,000 acres.
Map# 8: Propaganda Maps
Propaganda maps were in wide use in the 1900s and used to convey political messages and views of many contentious issues. The propaganda map above depicts a red pump/octopus as a metaphor for Western Europeans who took it upon themselves to communicate in any way with Eastern Europeans (the enemy). The map is rife with imagery of traitors and spies, and products being secretly given, sold, or provided to the enemy.
Map# 7: Hypsometric Map
Map# 6: PLSS (Public Land Survey System) Map
The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is a land partioning system used in the United States. Land in the public domain (and some privately held land) throughout the U.S. is subdivided by guidelines of this rectangular system of surveys. Land is divided into 6-mile-square townships, and townships are further subdivided into 36 one-mile- square sections. Subdivision continues into quarter sections, quarter-quarter sections, or irregular government lots. Permanent markers or a monument denote the section corner. The PLSS maps sections above depict the subdivisions.
Map# 5: Cadastral Maps
Cadastral maps depict boundaries and ownership of land parcels. They can include survey district names, unique identifying numbers for parcels, certificate of title numbers, positions of existing structures, section and/or lot numbers and their respective areas, adjoining and adjacent street names. They provide the location, and dimensions of various parcels of land. Their primary use is to document land ownership, value property,and determine taxes. They are frequently used in legal cases involving disputes over land ownership. The simple cadastral map above shows locations and sizes of various plots of land.
Map# 4: Thematic Map
Thematic maps highlight specific subjects. There are different types of thematic maps which can include choropleth or shaded maps, dot maps, proportional symbol maps, and isarithmic maps. These maps can also focus on a specific subject. The theme of the above map is Tall Buildings and it highlights the tallest buildings in the world.
Map# 3: Topographic Map
Topographic maps utilize contour lines to depict the shape and various elevations of land. They depict both natural and man made elements. Some of the features you can expect to find on a topographic map are: mountains, valleys, plains, lakes, rivers, and vegetation, roads, boundaries, transmission lines, and major buildings. The most common scale for these maps is 1:24,000. This is a map of the Big Meadows area of the Skyline Drive in Virginia. Notice how close many of the countour lines are, helping you to see the steepness of the terrain.
Monday, September 15, 2008
Map#2: Planemetric Map
Planemetric maps effectively show the footprints of buildings, sidewalks, parking lots, key thoroughfares. This type of map would be useful for depicting key buildings and locations on a University Campus, or a downtown area. This is a map of a portion of the Pensacola Junior College Campus showing key buildings, parking areas, and roads.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)